操作系统兼容性
我们建议在 Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 或使用systemd的基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版上安装 OpenSearch ,例如 CentOS、Amazon Linux 2 和 Ubuntu Long-Term Support (LTS)。OpenSearch 应该适用于大多数 Linux 发行版,但我们只测试了少数几个。对于任何版本的 OpenSearch,我们建议使用 RHEL 7 或 8、CentOS 7 或 8、Amazon Linux 2、Ubuntu 16.04、18.04 或 20.04。
Java 兼容性
适用于 Linux 的 OpenSearch 发行版在目录中附带了兼容的Adoptium JDK版本的 Java 。jdk要查找 JDK 版本,请运行./jdk/bin/java -version. 例如,OpenSearch 1.0.0 tarball 随附 Java 15.0.1+9(非 LTS),OpenSearch 1.3.0 随附 Java 11.0.14.1+1 (LTS),OpenSearch 2.0.0 随附 Java 17.0.2 +8 (LTS)。OpenSearch 使用所有兼容的 Java 版本进行了测试。
| 1.0 – 1.2.x | 11, 15 | 15.0.1+9 |
| 1.3.x | 8, 11, 14 | 11.0.14.1+1 |
| 2.0.0 | 11, 17 | 17.0.2+8 |
docker安装
创建docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
opensearch-node1:
image: opensearchproject/opensearch:2.2.0
container_name: opensearch-node1
environment:
– cluster.name=opensearch-cluster
– node.name=opensearch-node1
– discovery.seed_hosts=opensearch-node1,opensearch-node2
– cluster.initial_master_nodes=opensearch-node1,opensearch-node2
– bootstrap.memory_lock=true # along with the memlock settings below, disables swapping
– "OPENSEARCH_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m" # minimum and maximum Java heap size, recommend setting both to 50% of system RAM
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
nofile:
soft: 65536 # maximum number of open files for the OpenSearch user, set to at least 65536 on modern systems
hard: 65536
volumes:
– opensearch-data1:/usr/share/opensearch/data
ports:
– 9200:9200
– 9600:9600 # required for Performance Analyzer
networks:
– opensearch-net
opensearch-node2:
image: opensearchproject/opensearch:2.2.0
container_name: opensearch-node2
environment:
– cluster.name=opensearch-cluster
– node.name=opensearch-node2
– discovery.seed_hosts=opensearch-node1,opensearch-node2
– cluster.initial_master_nodes=opensearch-node1,opensearch-node2
– bootstrap.memory_lock=true
– "OPENSEARCH_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
nofile:
soft: 65536
hard: 65536
volumes:
– opensearch-data2:/usr/share/opensearch/data
networks:
– opensearch-net
opensearch-dashboards:
image: opensearchproject/opensearch-dashboards:2.2.0
container_name: opensearch-dashboards
ports:
– 5601:5601
expose:
– "5601"
environment:
OPENSEARCH_HOSTS: '["https://opensearch-node1:9200","https://opensearch-node2:9200"]' # must be a string with no spaces when specified as an environment variable
networks:
– opensearch-net
volumes:
opensearch-data1:
opensearch-data2:
networks:
opensearch-net:
启动集群
docker-compose up
启动日志 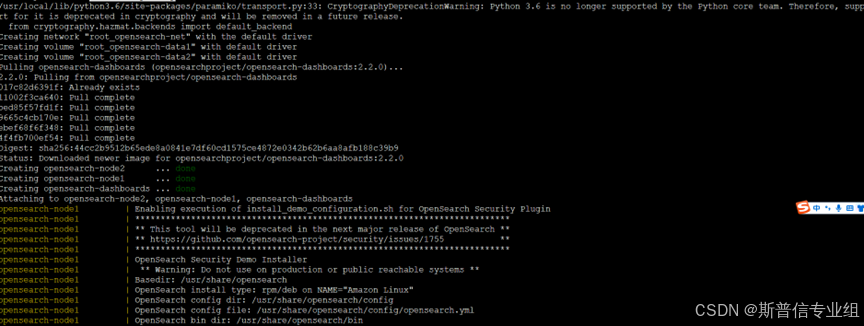 看到以下信息并且日志没明显error说明启动成功
看到以下信息并且日志没明显error说明启动成功 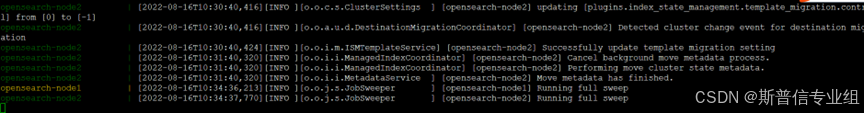 查看集群节点
查看集群节点  通过opensearch-dashboard查看
通过opensearch-dashboard查看 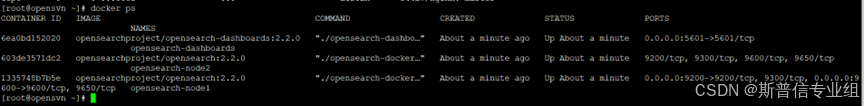 访问服务器的5601端口 用户名密码为admin admin
访问服务器的5601端口 用户名密码为admin admin 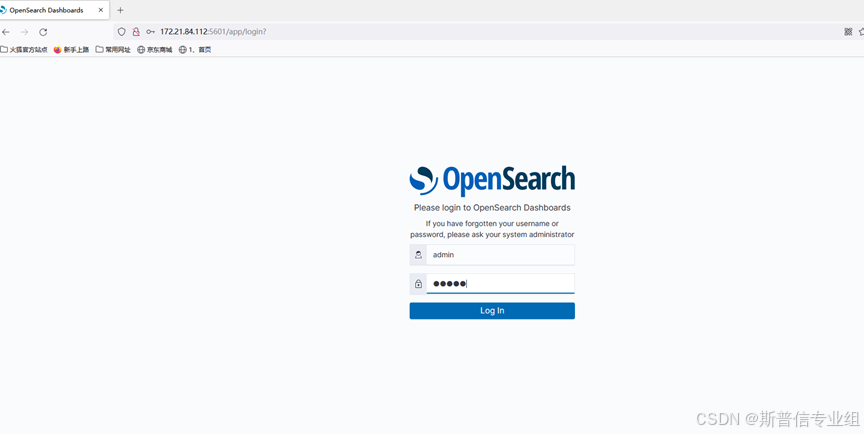 进入opensearch-dashboard页面
进入opensearch-dashboard页面 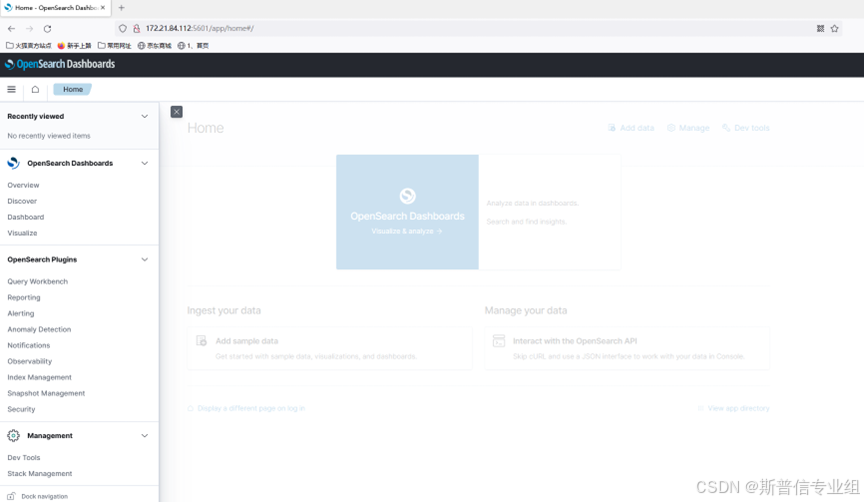 停止集群
停止集群
docker-compose down
停止集群并删除所有数据信息
docker-compose down -v
裸服务器安装
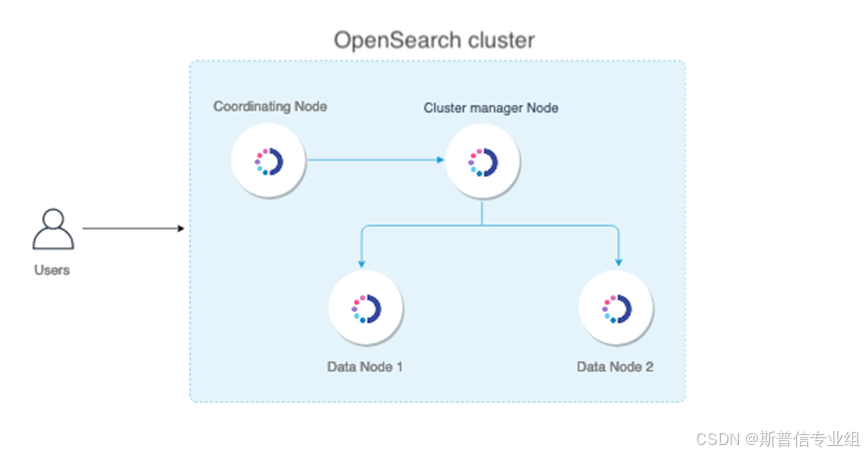
设计集群的方法有很多种组合。 下图显示了一个基本架构,其中包括一个四节点集群,该集群具有一个集群管理器节点、一个协调节点和两个数据节点。 更多节点信息请参照配置详解。
集群架构
服务器规划
| 172.21.84.119 | 2C 4G 100G SATA | Cluster manager data ingest |
| 172.21.84.120 | 2C 4G 100G SATA | Cluster manager data ingest |
| 172.21.84.121 | 2C 4G 100G SATA | Cluster manager data ingest |
进群之间请确保以下端口是连通的。 需要为 OpenSearch 组件打开以下端口。
| 443 | AWS OpenSearch Service 中的 OpenSearch 仪表板,具有传输中加密 (TLS) |
| 5601 | 开放搜索仪表板 |
| 9200 | 开放搜索 REST API |
| 9250 | 跨集群搜索 |
| 9300 | 节点通信和传输 |
| 9600 | 性能分析器 |
安装步骤
172.21.84.119 配置文件
cluster.name: bigdata
node.name: master01
node.roles: [cluster_manager ,data, ingest]
path.data: /data/opensearch/opensearch-2.2.0/data
path.logs: /data/opensearch/opensearch-2.2.0/logs
network.host: 172.21.84.119
http.port: 9200
discovery.seed_hosts: ["master01", "node01", "node02"]
cluster.initial_cluster_manager_nodes: ["master01", "node01", "node02"]
plugins.security.ssl.transport.pemcert_filepath: esnode.pem
plugins.security.ssl.transport.pemkey_filepath: esnode-key.pem
plugins.security.ssl.transport.pemtrustedcas_filepath: root-ca.pem
plugins.security.ssl.transport.enforce_hostname_verification: false
plugins.security.ssl.http.enabled: true
plugins.security.ssl.http.pemcert_filepath: esnode.pem
plugins.security.ssl.http.pemkey_filepath: esnode-key.pem
plugins.security.ssl.http.pemtrustedcas_filepath: root-ca.pem
plugins.security.allow_unsafe_democertificates: true
plugins.security.allow_default_init_securityindex: true
plugins.security.authcz.admin_dn:
CN=kirk,OU=client,O=client,L=test, C=de
plugins.security.audit.type: internal_opensearch
plugins.security.enable_snapshot_restore_privilege: true
plugins.security.check_snapshot_restore_write_privileges: true
plugins.security.restapi.roles_enabled: ["all_access", "security_rest_api_access"]
plugins.security.system_indices.enabled: true
plugins.security.system_indices.indices: [".plugins-ml-model", ".plugins-ml-task", ".opendistro-alerting-config", ".opendistro-alerting-alert*", ".opendistro-anomaly-results*", ".opendistro-anomaly-detector*", ".opendistro-anomaly-checkpoints", ".opendistro-anomaly-detection-state", ".opendistro-reports-", ".opensearch-notifications-", ".opensearch-notebooks", ".opensearch-observability", ".opendistro-asynchronous-search-response*", ".replication-metadata-store"]
node.max_local_storage_nodes: 3
172.21.84.120 配置文件
注: 相同配置不再展示
cluster.name: bigdata
node.name: master01
node.roles: [cluster_manager ,data, ingest]
path.data: /data/opensearch/opensearch-2.2.0/data
path.logs: /data/opensearch/opensearch-2.2.0/logs
network.host: 172.21.84.120
172.21.84.121 配置文件
cluster.name: bigdata
node.name: master01
node.roles: [cluster_manager ,data, ingest]
path.data: /data/opensearch/opensearch-2.2.0/data
path.logs: /data/opensearch/opensearch-2.2.0/logs
network.host: 172.21.84.121
依次启动三台openserach
su – opensearch -c "/data/opensearch/opensearch-2.2.0/bin/opensearch"
看到如下信息,集群创建成功 
查看集群
查看节点信息 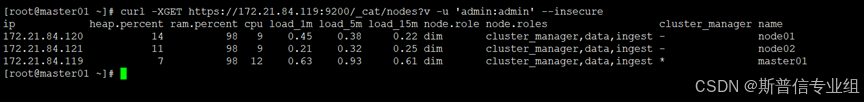 查看集群健康状态
查看集群健康状态  至此裸金属版部署完成
至此裸金属版部署完成
Helm安装
官方安装
请确保k8s集群安装了helm命令,且可以链接外网。默认 Helm 部署一个三节点集群。我们建议您为此部署至少有 8 GiB 的可用内存。 例如,如果可用内存少于 4 GiB,可能会部署会失败。 版本要求
- Kubernetes >= 1.14
- Helm >= 2.17.0
Kubernetes 中部署 NFS-Subdir-External-Provisioner 为 NFS 提供动态分配卷  并且自动绑定pv,pvc,若绑定失败需执行
并且自动绑定pv,pvc,若绑定失败需执行
kubectl patch storageclass nfs-storage -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
安装步骤

helm repo update

helm search repo opensearch

helm install my-deployment opensearch/opensearch
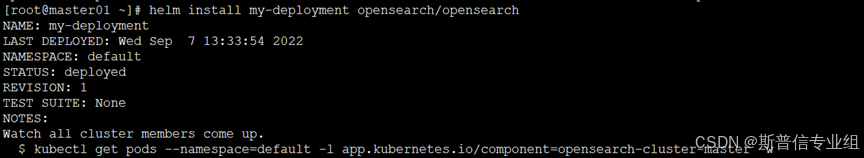 查看部署的pod
查看部署的pod 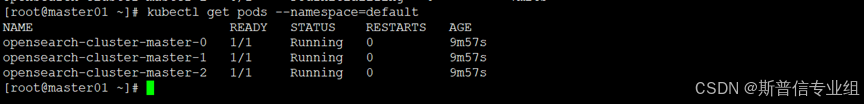 确认节点运行状态
确认节点运行状态 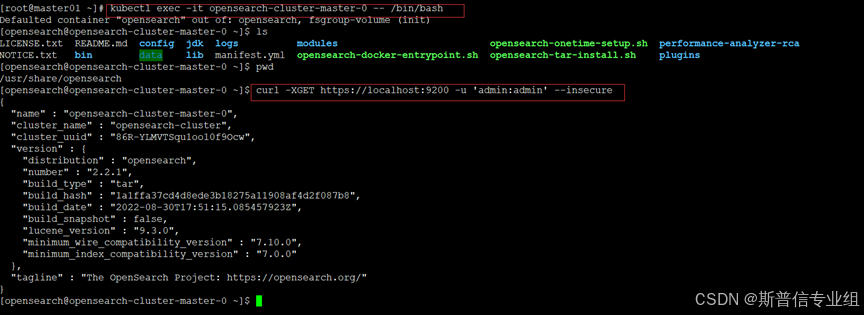 卸载opensearch
卸载opensearch  运行 helm delete my-deployment
运行 helm delete my-deployment
自定义安装
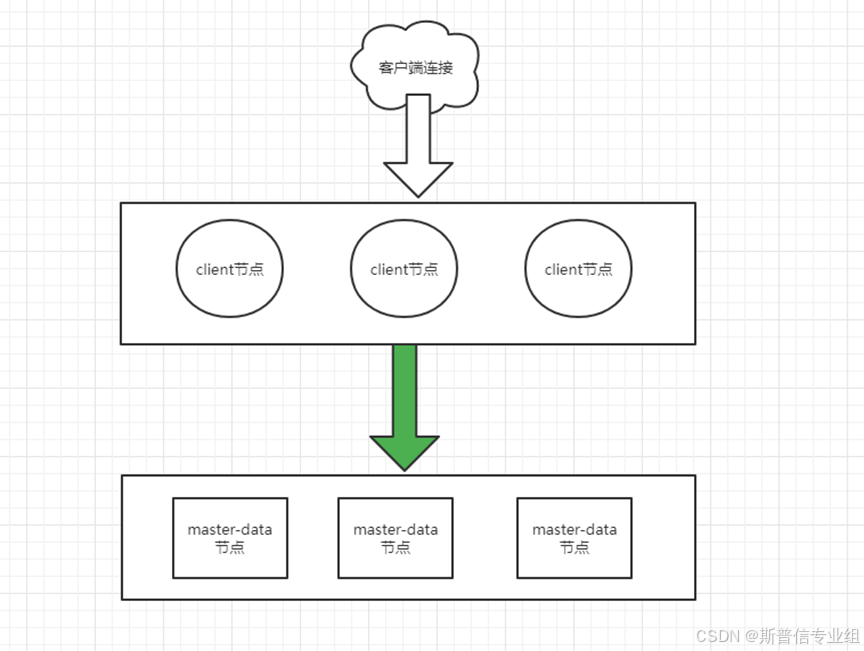 其中data节点也可拆分出来本文不做展示。
其中data节点也可拆分出来本文不做展示。
openserach-master.yaml
—
clusterName: "opensearch-cluster"
nodeGroup: "master"
# If discovery.type in the opensearch configuration is set to "single-node",
# this should be set to "true"
# If "true", replicas will be forced to 1
singleNode: false
# The service that non master groups will try to connect to when joining the cluster
# This should be set to clusterName + "-" + nodeGroup for your master group
masterService: "opensearch-cluster-master"
# OpenSearch roles that will be applied to this nodeGroup
# These will be set as environment variable "node.roles". E.g. node.roles=master,ingest,data,remote_cluster_client
roles:
– master
– ingest
– data
replicas: 3
# if not set, falls back to parsing .Values.imageTag, then .Chart.appVersion.
majorVersion: ""
global:
# Set if you want to change the default docker registry, e.g. a private one.
dockerRegistry: ""
# Allows you to add any config files in {{ .Values.opensearchHome }}/config
opensearchHome: /usr/share/opensearch
# such as opensearch.yml and log4j2.properties
config:
# Values must be YAML literal style scalar / YAML multiline string.
# <filename>: |
# <formatted-value(s)>
# log4j2.properties: |
# status = error
#
# appender.console.type = Console
# appender.console.name = console
# appender.console.layout.type = PatternLayout
# appender.console.layout.pattern = [%d{ISO8601}][%-5p][%-25c{1.}] [%node_name]%marker %m%n
#
# rootLogger.level = info
# rootLogger.appenderRef.console.ref = console
opensearch.yml: |
cluster.name: opensearch-cluster
# Bind to all interfaces because we don't know what IP address Docker will assign to us.
network.host: 0.0.0.0
# Setting network.host to a non-loopback address enables the annoying bootstrap checks. "Single-node" mode disables them again.
# Implicitly done if ".singleNode" is set to "true".
# discovery.type: single-node
# Start OpenSearch Security Demo Configuration
# WARNING: revise all the lines below before you go into production
plugins:
security:
ssl:
transport:
pemcert_filepath: esnode.pem
pemkey_filepath: esnode-key.pem
pemtrustedcas_filepath: root-ca.pem
enforce_hostname_verification: false
http:
enabled: true
pemcert_filepath: esnode.pem
pemkey_filepath: esnode-key.pem
pemtrustedcas_filepath: root-ca.pem
allow_unsafe_democertificates: true
allow_default_init_securityindex: true
authcz:
admin_dn:
– CN=kirk,OU=client,O=client,L=test,C=de
audit.type: internal_opensearch
enable_snapshot_restore_privilege: true
check_snapshot_restore_write_privileges: true
restapi:
roles_enabled: ["all_access", "security_rest_api_access"]
system_indices:
enabled: true
indices:
[
".opendistro-alerting-config",
".opendistro-alerting-alert*",
".opendistro-anomaly-results*",
".opendistro-anomaly-detector*",
".opendistro-anomaly-checkpoints",
".opendistro-anomaly-detection-state",
".opendistro-reports-*",
".opendistro-notifications-*",
".opendistro-notebooks",
".opendistro-asynchronous-search-response*",
]
######## End OpenSearch Security Demo Configuration ########
# log4j2.properties:
# Extra environment variables to append to this nodeGroup
# This will be appended to the current 'env:' key. You can use any of the kubernetes env
# syntax here
extraEnvs: []
# – name: MY_ENVIRONMENT_VAR
# value: the_value_goes_here
# Allows you to load environment variables from kubernetes secret or config map
envFrom: []
# – secretRef:
# name: env-secret
# – configMapRef:
# name: config-map
# A list of secrets and their paths to mount inside the pod
# This is useful for mounting certificates for security and for mounting
# the X-Pack license
secretMounts: []
hostAliases: []
# – ip: "127.0.0.1"
# hostnames:
# – "foo.local"
# – "bar.local"
image:
repository: "opensearchproject/opensearch"
# override image tag, which is .Chart.AppVersion by default
tag: ""
pullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
podAnnotations: {}
# iam.amazonaws.com/role: es-cluster
# additionals labels
labels: {}
opensearchJavaOpts: "-Xmx512M -Xms512M"
resources:
requests:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "100Mi"
initResources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: "25m"
# memory: "128Mi"
# requests:
# cpu: "25m"
# memory: "128Mi"
sidecarResources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: "25m"
# memory: "128Mi"
# requests:
# cpu: "25m"
# memory: "128Mi"
networkHost: "0.0.0.0"
rbac:
create: false
serviceAccountAnnotations: {}
serviceAccountName: ""
podSecurityPolicy:
create: false
name: ""
spec:
privileged: true
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
seLinux:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
volumes:
– secret
– configMap
– persistentVolumeClaim
– emptyDir
persistence:
enabled: true
# Set to false to disable the `fsgroup-volume` initContainer that will update permissions on the persistent disk.
enableInitChown: true
# override image, which is busybox by default
# image: busybox
# override image tag, which is latest by default
# imageTag:
labels:
# Add default labels for the volumeClaimTemplate of the StatefulSet
enabled: false
# OpenSearch Persistent Volume Storage Class
# If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
# If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
# If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
# set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
# GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
#
# storageClass: "-"
accessModes:
– ReadWriteOnce
size: 5Gi
annotations: {}
extraVolumes: []
# – name: extras
# emptyDir: {}
extraVolumeMounts: []
# – name: extras
# mountPath: /usr/share/extras
# readOnly: true
extraContainers: []
# – name: do-something
# image: busybox
# command: ['do', 'something']
extraInitContainers: []
# – name: do-somethings
# image: busybox
# command: ['do', 'something']
# This is the PriorityClass settings as defined in
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/pod-priority-preemption/#priorityclass
priorityClassName: ""
# By default this will make sure two pods don't end up on the same node
# Changing this to a region would allow you to spread pods across regions
antiAffinityTopologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
# Hard means that by default pods will only be scheduled if there are enough nodes for them
# and that they will never end up on the same node. Setting this to soft will do this "best effort"
antiAffinity: "soft"
# This is the node affinity settings as defined in
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#node-affinity-beta-feature
nodeAffinity: {}
# This is the pod topology spread constraints
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-topology-spread-constraints/
topologySpreadConstraints: []
# The default is to deploy all pods serially. By setting this to parallel all pods are started at
# the same time when bootstrapping the cluster
podManagementPolicy: "Parallel"
# The environment variables injected by service links are not used, but can lead to slow OpenSearch boot times when
# there are many services in the current namespace.
# If you experience slow pod startups you probably want to set this to `false`.
enableServiceLinks: true
protocol: https
httpPort: 9200
transportPort: 9300
service:
labels: {}
labelsHeadless: {}
headless:
annotations: {}
type: ClusterIP
nodePort: ""
annotations: {}
httpPortName: http
transportPortName: transport
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
externalTrafficPolicy: ""
updateStrategy: RollingUpdate
# This is the max unavailable setting for the pod disruption budget
# The default value of 1 will make sure that kubernetes won't allow more than 1
# of your pods to be unavailable during maintenance
maxUnavailable: 1
podSecurityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
runAsUser: 1000
securityContext:
capabilities:
drop:
– ALL
# readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
securityConfig:
enabled: true
path: "/usr/share/opensearch/plugins/opensearch-security/securityconfig"
actionGroupsSecret:
configSecret:
internalUsersSecret:
rolesSecret:
rolesMappingSecret:
tenantsSecret:
# The following option simplifies securityConfig by using a single secret and
# specifying the config files as keys in the secret instead of creating
# different secrets for for each config file.
# Note that this is an alternative to the individual secret configuration
# above and shouldn't be used if the above secrets are used.
config:
# There are multiple ways to define the configuration here:
# * If you define anything under data, the chart will automatically create
# a secret and mount it.
# * If you define securityConfigSecret, the chart will assume this secret is
# created externally and mount it.
# * It is an error to define both data and securityConfigSecret.
securityConfigSecret: ""
dataComplete: true
data: {}
# config.yml: |-
# internal_users.yml: |-
# roles.yml: |-
# roles_mapping.yml: |-
# action_groups.yml: |-
# tenants.yml: |-
# How long to wait for opensearch to stop gracefully
terminationGracePeriod: 120
sysctlVmMaxMapCount: 262144
startupProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 9200
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 3
failureThreshold: 30
readinessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 9200
periodSeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 3
failureThreshold: 3
## Use an alternate scheduler.
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-multiple-schedulers/
##
schedulerName: ""
imagePullSecrets: []
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
# Enabling this will publically expose your OpenSearch instance.
# Only enable this if you have security enabled on your cluster
ingress:
enabled: false
# For Kubernetes >= 1.18 you should specify the ingress-controller via the field ingressClassName
# See https://kubernetes.io/blog/2020/04/02/improvements-to-the-ingress-api-in-kubernetes-1.18/#specifying-the-class-of-an-ingress
# ingressClassName: nginx
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
path: /
hosts:
– chart-example.local
tls: []
# – secretName: chart-example-tls
# hosts:
# – chart-example.local
nameOverride: ""
fullnameOverride: ""
masterTerminationFix: false
lifecycle: {}
# preStop:
# exec:
# command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo Hello from the postStart handler > /usr/share/message"]
# postStart:
# exec:
# command:
# – bash
# – -c
# – |
# #!/bin/bash
# # Add a template to adjust number of shards/replicas1
# TEMPLATE_NAME=my_template
# INDEX_PATTERN="logstash-*"
# SHARD_COUNT=8
# REPLICA_COUNT=1
# ES_URL=http://localhost:9200
# while [[ "$(curl -s -o /dev/null -w '%{http_code}\\n' $ES_URL)" != "200" ]]; do sleep 1; done
# curl -XPUT "$ES_URL/_template/$TEMPLATE_NAME" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'{"index_patterns":['\\""$INDEX_PATTERN"\\"'],"settings":{"number_of_shards":'$SHARD_COUNT',"number_of_replicas":'$REPLICA_COUNT'}}'
keystore: []
# To add secrets to the keystore:
# – secretName: opensearch-encryption-key
networkPolicy:
create: false
## Enable creation of NetworkPolicy resources. Only Ingress traffic is filtered for now.
## In order for a Pod to access OpenSearch, it needs to have the following label:
## {{ template "uname" . }}-client: "true"
## Example for default configuration to access HTTP port:
## opensearch-master-http-client: "true"
## Example for default configuration to access transport port:
## opensearch-master-transport-client: "true"
http:
enabled: false
# Deprecated
# please use the above podSecurityContext.fsGroup instead
fsGroup: ""
## Set optimal sysctl's. This requires privilege. Can be disabled if
## the system has already been preconfigured. (Ex: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/vm-max-map-count.html)
## Also see: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/sysctl-cluster/
sysctl:
enabled: false
## Enable to add 3rd Party / Custom plugins not offered in the default OpenSearch image.
plugins:
enabled: false
installList: []
# – example-fake-plugin
# — Array of extra K8s manifests to deploy
extraObjects: []
# – apiVersion: secrets-store.csi.x-k8s.io/v1
# kind: SecretProviderClass
# metadata:
# name: argocd-secrets-store
# spec:
# provider: aws
# parameters:
# objects: |
# – objectName: "argocd"
# objectType: "secretsmanager"
# jmesPath:
# – path: "client_id"
# objectAlias: "client_id"
# – path: "client_secret"
# objectAlias: "client_secret"
# secretObjects:
# – data:
# – key: client_id
# objectName: client_id
# – key: client_secret
# objectName: client_secret
# secretName: argocd-secrets-store
# type: Opaque
# labels:
# app.kubernetes.io/part-of: argocd
安装命令 注:version并非opensearch版本,而是CHART VERSION 
helm install opensearch-master -f openserach-master.yaml –version 2.5.1 opensearch/opensearch
opensearch-client.yaml
—
clusterName: "opensearch-cluster"
nodeGroup: "client"
# If discovery.type in the opensearch configuration is set to "single-node",
# this should be set to "true"
# If "true", replicas will be forced to 1
singleNode: false
# The service that non master groups will try to connect to when joining the cluster
# This should be set to clusterName + "-" + nodeGroup for your master group
masterService: "opensearch-cluster-master"
# OpenSearch roles that will be applied to this nodeGroup
# These will be set as environment variable "node.roles". E.g. node.roles=master,ingest,data,remote_cluster_client
roles:
– remote_cluster_client
replicas: 2
# if not set, falls back to parsing .Values.imageTag, then .Chart.appVersion.
majorVersion: ""
global:
# Set if you want to change the default docker registry, e.g. a private one.
dockerRegistry: ""
# Allows you to add any config files in {{ .Values.opensearchHome }}/config
opensearchHome: /usr/share/opensearch
# such as opensearch.yml and log4j2.properties
config:
# Values must be YAML literal style scalar / YAML multiline string.
# <filename>: |
# <formatted-value(s)>
# log4j2.properties: |
# status = error
#
# appender.console.type = Console
# appender.console.name = console
# appender.console.layout.type = PatternLayout
# appender.console.layout.pattern = [%d{ISO8601}][%-5p][%-25c{1.}] [%node_name]%marker %m%n
#
# rootLogger.level = info
# rootLogger.appenderRef.console.ref = console
opensearch.yml: |
cluster.name: opensearch-cluster
# Bind to all interfaces because we don't know what IP address Docker will assign to us.
network.host: 0.0.0.0
# Setting network.host to a non-loopback address enables the annoying bootstrap checks. "Single-node" mode disables them again.
# Implicitly done if ".singleNode" is set to "true".
# discovery.type: single-node
# Start OpenSearch Security Demo Configuration
# WARNING: revise all the lines below before you go into production
plugins:
security:
ssl:
transport:
pemcert_filepath: esnode.pem
pemkey_filepath: esnode-key.pem
pemtrustedcas_filepath: root-ca.pem
enforce_hostname_verification: false
http:
enabled: true
pemcert_filepath: esnode.pem
pemkey_filepath: esnode-key.pem
pemtrustedcas_filepath: root-ca.pem
allow_unsafe_democertificates: true
allow_default_init_securityindex: true
authcz:
admin_dn:
– CN=kirk,OU=client,O=client,L=test,C=de
audit.type: internal_opensearch
enable_snapshot_restore_privilege: true
check_snapshot_restore_write_privileges: true
restapi:
roles_enabled: ["all_access", "security_rest_api_access"]
system_indices:
enabled: true
indices:
[
".opendistro-alerting-config",
".opendistro-alerting-alert*",
".opendistro-anomaly-results*",
".opendistro-anomaly-detector*",
".opendistro-anomaly-checkpoints",
".opendistro-anomaly-detection-state",
".opendistro-reports-*",
".opendistro-notifications-*",
".opendistro-notebooks",
".opendistro-asynchronous-search-response*",
]
######## End OpenSearch Security Demo Configuration ########
# log4j2.properties:
# Extra environment variables to append to this nodeGroup
# This will be appended to the current 'env:' key. You can use any of the kubernetes env
# syntax here
extraEnvs: []
# – name: MY_ENVIRONMENT_VAR
# value: the_value_goes_here
# Allows you to load environment variables from kubernetes secret or config map
envFrom: []
# – secretRef:
# name: env-secret
# – configMapRef:
# name: config-map
# A list of secrets and their paths to mount inside the pod
# This is useful for mounting certificates for security and for mounting
# the X-Pack license
secretMounts: []
hostAliases: []
# – ip: "127.0.0.1"
# hostnames:
# – "foo.local"
# – "bar.local"
image:
repository: "opensearchproject/opensearch"
# override image tag, which is .Chart.AppVersion by default
tag: ""
pullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
podAnnotations: {}
# iam.amazonaws.com/role: es-cluster
# additionals labels
labels: {}
opensearchJavaOpts: "-Xmx512M -Xms512M"
resources:
requests:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "100Mi"
initResources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: "25m"
# memory: "128Mi"
# requests:
# cpu: "25m"
# memory: "128Mi"
sidecarResources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: "25m"
# memory: "128Mi"
# requests:
# cpu: "25m"
# memory: "128Mi"
networkHost: "0.0.0.0"
rbac:
create: false
serviceAccountAnnotations: {}
serviceAccountName: ""
podSecurityPolicy:
create: false
name: ""
spec:
privileged: true
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
seLinux:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
volumes:
– secret
– configMap
– persistentVolumeClaim
– emptyDir
persistence:
enabled: false
# Set to false to disable the `fsgroup-volume` initContainer that will update permissions on the persistent disk.
enableInitChown: false
# override image, which is busybox by default
# image: busybox
# override image tag, which is latest by default
# imageTag:
labels:
# Add default labels for the volumeClaimTemplate of the StatefulSet
enabled: false
# OpenSearch Persistent Volume Storage Class
# If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
# If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
# If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
# set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
# GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
#
# storageClass: "-"
accessModes:
– ReadWriteOnce
size: 1Gi
annotations: {}
extraVolumes: []
# – name: extras
# emptyDir: {}
extraVolumeMounts: []
# – name: extras
# mountPath: /usr/share/extras
# readOnly: true
extraContainers: []
# – name: do-something
# image: busybox
# command: ['do', 'something']
extraInitContainers: []
# – name: do-somethings
# image: busybox
# command: ['do', 'something']
# This is the PriorityClass settings as defined in
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/pod-priority-preemption/#priorityclass
priorityClassName: ""
# By default this will make sure two pods don't end up on the same node
# Changing this to a region would allow you to spread pods across regions
antiAffinityTopologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
# Hard means that by default pods will only be scheduled if there are enough nodes for them
# and that they will never end up on the same node. Setting this to soft will do this "best effort"
antiAffinity: "soft"
# This is the node affinity settings as defined in
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#node-affinity-beta-feature
nodeAffinity: {}
# This is the pod topology spread constraints
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-topology-spread-constraints/
topologySpreadConstraints: []
# The default is to deploy all pods serially. By setting this to parallel all pods are started at
# the same time when bootstrapping the cluster
podManagementPolicy: "Parallel"
# The environment variables injected by service links are not used, but can lead to slow OpenSearch boot times when
# there are many services in the current namespace.
# If you experience slow pod startups you probably want to set this to `false`.
enableServiceLinks: true
protocol: https
httpPort: 9200
transportPort: 9300
service:
type: NodePort
nodePort: "30601"
updateStrategy: RollingUpdate
# This is the max unavailable setting for the pod disruption budget
# The default value of 1 will make sure that kubernetes won't allow more than 1
# of your pods to be unavailable during maintenance
maxUnavailable: 1
podSecurityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
runAsUser: 1000
securityContext:
capabilities:
drop:
– ALL
# readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
securityConfig:
enabled: true
path: "/usr/share/opensearch/plugins/opensearch-security/securityconfig"
actionGroupsSecret:
configSecret:
internalUsersSecret:
rolesSecret:
rolesMappingSecret:
tenantsSecret:
# The following option simplifies securityConfig by using a single secret and
# specifying the config files as keys in the secret instead of creating
# different secrets for for each config file.
# Note that this is an alternative to the individual secret configuration
# above and shouldn't be used if the above secrets are used.
config:
# There are multiple ways to define the configuration here:
# * If you define anything under data, the chart will automatically create
# a secret and mount it.
# * If you define securityConfigSecret, the chart will assume this secret is
# created externally and mount it.
# * It is an error to define both data and securityConfigSecret.
securityConfigSecret: ""
dataComplete: true
data: {}
# config.yml: |-
# internal_users.yml: |-
# roles.yml: |-
# roles_mapping.yml: |-
# action_groups.yml: |-
# tenants.yml: |-
# How long to wait for opensearch to stop gracefully
terminationGracePeriod: 120
sysctlVmMaxMapCount: 262144
startupProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 9200
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 3
failureThreshold: 30
readinessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 9200
periodSeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 3
failureThreshold: 3
## Use an alternate scheduler.
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-multiple-schedulers/
##
schedulerName: ""
imagePullSecrets: []
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
# Enabling this will publically expose your OpenSearch instance.
# Only enable this if you have security enabled on your cluster
ingress:
enabled: false
# For Kubernetes >= 1.18 you should specify the ingress-controller via the field ingressClassName
# See https://kubernetes.io/blog/2020/04/02/improvements-to-the-ingress-api-in-kubernetes-1.18/#specifying-the-class-of-an-ingress
# ingressClassName: nginx
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
path: /
hosts:
– chart-example.local
tls: []
# – secretName: chart-example-tls
# hosts:
# – chart-example.local
nameOverride: ""
fullnameOverride: ""
masterTerminationFix: false
lifecycle: {}
# preStop:
# exec:
# command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo Hello from the postStart handler > /usr/share/message"]
# postStart:
# exec:
# command:
# – bash
# – -c
# – |
# #!/bin/bash
# # Add a template to adjust number of shards/replicas1
# TEMPLATE_NAME=my_template
# INDEX_PATTERN="logstash-*"
# SHARD_COUNT=8
# REPLICA_COUNT=1
# ES_URL=http://localhost:9200
# while [[ "$(curl -s -o /dev/null -w '%{http_code}\\n' $ES_URL)" != "200" ]]; do sleep 1; done
# curl -XPUT "$ES_URL/_template/$TEMPLATE_NAME" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'{"index_patterns":['\\""$INDEX_PATTERN"\\"'],"settings":{"number_of_shards":'$SHARD_COUNT',"number_of_replicas":'$REPLICA_COUNT'}}'
keystore: []
# To add secrets to the keystore:
# – secretName: opensearch-encryption-key
networkPolicy:
create: false
## Enable creation of NetworkPolicy resources. Only Ingress traffic is filtered for now.
## In order for a Pod to access OpenSearch, it needs to have the following label:
## {{ template "uname" . }}-client: "true"
## Example for default configuration to access HTTP port:
## opensearch-master-http-client: "true"
## Example for default configuration to access transport port:
## opensearch-master-transport-client: "true"
http:
enabled: false
# Deprecated
# please use the above podSecurityContext.fsGroup instead
fsGroup: ""
## Set optimal sysctl's. This requires privilege. Can be disabled if
## the system has already been preconfigured. (Ex: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/vm-max-map-count.html)
## Also see: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/sysctl-cluster/
sysctl:
enabled: false
## Enable to add 3rd Party / Custom plugins not offered in the default OpenSearch image.
plugins:
enabled: false
installList: []
# – example-fake-plugin
# — Array of extra K8s manifests to deploy
extraObjects: []
# – apiVersion: secrets-store.csi.x-k8s.io/v1
# kind: SecretProviderClass
# metadata:
# name: argocd-secrets-store
# spec:
# provider: aws
# parameters:
# objects: |
# – objectName: "argocd"
# objectType: "secretsmanager"
# jmesPath:
# – path: "client_id"
# objectAlias: "client_id"
# – path: "client_secret"
# objectAlias: "client_secret"
# secretObjects:
# – data:
# – key: client_id
# objectName: client_id
# – key: client_secret
# objectName: client_secret
# secretName: argocd-secrets-store
# type: Opaque
# labels:
# app.kubernetes.io/part-of: argocd
helm install opensearch-client -f openserach-client.yaml –version 2.5.1 opensearch/opensearch
访问测试 
yaml文件部署opensearch三节点
部署文件如下: os_cm.yml、os_headless.yml、os_statefulset_hostpath.yml、os_svc.yml
需要注意镜像地址可以拉取到,此方案采用的是hostpath方式需要每个pod节点创建目录,也可采用nfs共享目录方式做数据持久化。 执行
kubectl apply -f os_cm.yml
kubectl apply -f os_headless.yml
kubectl apply -f os_statefulset_hostpath.yml
kubectl apply -f os_svc.yml
查看文件内容
[root@master01 openserach_install]# cat os_cm.yml
apiVersion: v1
data:
opensearch.yml: |
cluster.name: opensearch-cluster
# Bind to all interfaces because we don't know what IP address Docker will assign to us.
network.host: 0.0.0.0
# Setting network.host to a non-loopback address enables the annoying bootstrap checks. "Single-node" mode disables them again.
# Implicitly done if ".singleNode" is set to "true".
# discovery.type: single-node
# Start OpenSearch Security Demo Configuration
# WARNING: revise all the lines below before you go into production
plugins:
security:
ssl:
transport:
pemcert_filepath: esnode.pem
pemkey_filepath: esnode-key.pem
pemtrustedcas_filepath: root-ca.pem
enforce_hostname_verification: false
http:
enabled: true
pemcert_filepath: esnode.pem
pemkey_filepath: esnode-key.pem
pemtrustedcas_filepath: root-ca.pem
allow_unsafe_democertificates: true
allow_default_init_securityindex: true
authcz:
admin_dn:
– CN=kirk,OU=client,O=client,L=test,C=de
audit.type: internal_opensearch
enable_snapshot_restore_privilege: true
check_snapshot_restore_write_privileges: true
restapi:
roles_enabled: ["all_access", "security_rest_api_access"]
system_indices:
enabled: true
indices:
[
".opendistro-alerting-config",
".opendistro-alerting-alert*",
".opendistro-anomaly-results*",
".opendistro-anomaly-detector*",
".opendistro-anomaly-checkpoints",
".opendistro-anomaly-detection-state",
".opendistro-reports-*",
".opendistro-notifications-*",
".opendistro-notebooks",
".opendistro-asynchronous-search-response*",
]
######## End OpenSearch Security Demo Configuration ########
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: opensearch-cluster-master
app.kubernetes.io/instance: opensearch-server
app.kubernetes.io/name: opensearch
name: opensearch-cluster-master-config
namespace: default
[root@master01 openserach_install]# cat os_headless.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
service.alpha.kubernetes.io/tolerate-unready-endpoints: "true"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: opensearch-cluster-master
app.kubernetes.io/instance: opensearch-server
app.kubernetes.io/name: opensearch
name: opensearch-cluster-master-headless
namespace: default
spec:
clusterIP: None
clusterIPs:
– None
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ipFamilies:
– IPv4
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
ports:
– name: http
port: 9200
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9200
– name: transport
port: 9300
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9300
publishNotReadyAddresses: true
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: opensearch-server
app.kubernetes.io/name: opensearch
sessionAffinity: None
cat os_statefulset_hostpath.yml
apiVersion: v1
items:
– apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
annotations:
majorVersion: "2"
generation: 1
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: opensearch-cluster-master
app.kubernetes.io/instance: opensearch-server
app.kubernetes.io/name: opensearch
name: opensearch-cluster-master
namespace: default
spec:
podManagementPolicy: Parallel
replicas: 3
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: opensearch-server
app.kubernetes.io/name: opensearch
serviceName: opensearch-cluster-master-headless
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: opensearch-cluster-master
app.kubernetes.io/instance: opensearch-server
app.kubernetes.io/name: opensearch
name: opensearch-cluster-master
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
– podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
– key: app.kubernetes.io/instance
operator: In
values:
– opensearch-server
– key: app.kubernetes.io/name
operator: In
values:
– opensearch
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
weight: 1
containers:
– env:
– name: node.name
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.name
– name: cluster.initial_master_nodes
value: opensearch-cluster-master-0,opensearch-cluster-master-1,opensearch-cluster-master-2,
– name: discovery.seed_hosts
value: opensearch-cluster-master-headless
– name: cluster.name
value: opensearch-cluster
– name: network.host
value: 0.0.0.0
– name: OPENSEARCH_JAVA_OPTS
value: -Xmx512M -Xms512M
– name: node.roles
value: master,ingest,data,remote_cluster_client,
image: opensearchproject/opensearch:2.0.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: opensearch
ports:
– containerPort: 9200
name: http
protocol: TCP
– containerPort: 9300
name: transport
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
periodSeconds: 5
successThreshold: 1
tcpSocket:
port: 9200
timeoutSeconds: 3
resources:
requests:
cpu: "1"
memory: 100Mi
securityContext:
capabilities:
drop:
– ALL
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
startupProbe:
failureThreshold: 30
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
tcpSocket:
port: 9200
timeoutSeconds: 3
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
– mountPath: /usr/share/opensearch/data
name: opensearch-cluster-master
– mountPath: /usr/share/opensearch/config/opensearch.yml
name: config
subPath: opensearch.yml
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
enableServiceLinks: true
initContainers:
– args:
– chown -R 1000:1000 /usr/share/opensearch/data
command:
– sh
– -c
image: busybox:latest
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: fsgroup-volume
resources: {}
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
– mountPath: /usr/share/opensearch/data
name: opensearch-cluster-master
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
runAsUser: 1000
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 120
volumes:
– configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: opensearch-cluster-master-config
name: config
– hostPath:
path: /tmp/osdata
name: opensearch-cluster-master
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
kind: List
cat os_svc.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: opensearch-cluster-master
app.kubernetes.io/instance: opensearch-server
app.kubernetes.io/name: opensearch
name: opensearch-cluster-master
namespace: default
spec:
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ipFamilies:
– IPv4
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
ports:
– name: http
port: 9200
nodePort: 32001
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9200
– name: transport
port: 9300
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9300
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: opensearch-server
app.kubernetes.io/name: opensearch
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心



评论前必须登录!
注册