目录
1. 功能了解
1.1. 啥是 dic_server?
1.2. dic_server 的小目标
2. 基本框架
2.1. 基本文件框架
2.2. 业务与服务器解耦 -> 回调函数
3. 字典
3.1. 字典配置文件
3.2. 构建字典类
3.2.1. 字典类的基本成员
3.2.2. 字典类构造
3.2.2.1. 构造
3.2.2.2. 信息加载
3.2.2.2.1. 先打开文件:
3.2.2.2.2. 如果打开失败了呢?
3.2.2.2.3. 打开成功呢?
3.2.2.2.4. 最后记得关闭文件描述符 -> 防止资源泄露
3.2.3. dict::translate()
3.2.3.1. 查找一个空单词?
3.2.3.2. 如果没查到?
3.2.3.3. 如果查到了?
3.3. 字典服务 与 服务器相关联
3.4. 测试一下
4. 参考代码
4.1. 核心代码
4.2. 其他代码
目标:
- 基于udp的服务器接口基本认识
- 实现服务器(收消息发消息) 与 业务(翻译业务)的分离逻辑 -> 通过回调函数实现.
1. 功能了解
1.1. 啥是 dic_server?
dic_server: 基于 udp 套接字的基本业务 -> 英汉翻译.

1.2. dic_server 的小目标
2. 基本框架
2.1. 基本文件框架
为了方便, 我们直接把 udp_echo_server 的一些代码 CV 过来即可.

2.2. 业务与服务器解耦 -> 回调函数
约定: 客户端发来的是单词.
这里为了方便解耦, 我们用一下包装器包装函数, 来达到方便类型统一的目的.

注意: 参数是非const参数.
如何用呢? 用户传对应的业务给服务器, 这样就实现解耦了(实现的是业务和服务器之间的逻辑解耦).

回调函数调用完成之后, 我们服务器再返回即可.
3. 字典
3.1. 字典配置文件
3.2. 构建字典类
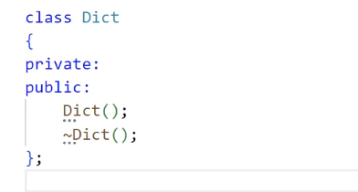
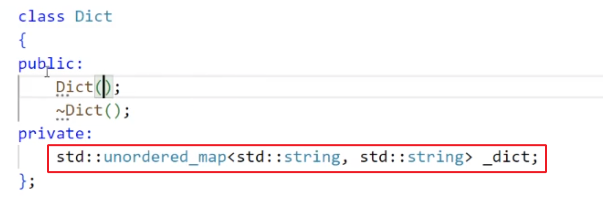
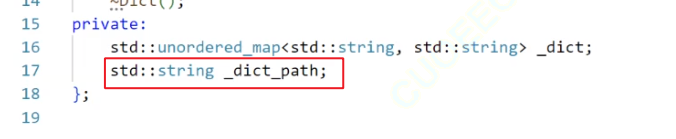
3.2.1. 字典类的基本成员
3.2.2. 字典类构造
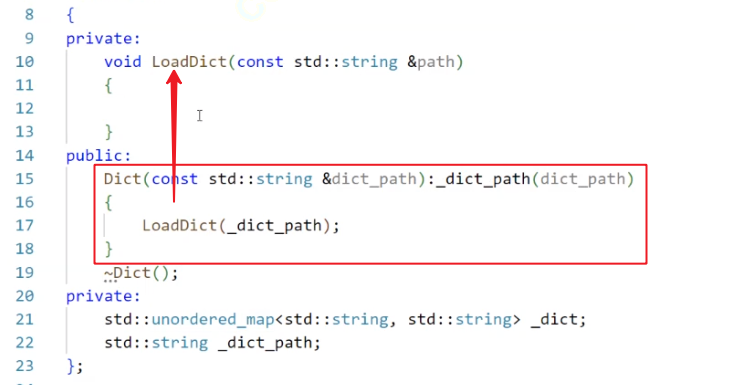
3.2.2.1. 构造
告诉构造配置文件路径, 然后开始加载:
3.2.2.2. 信息加载
3.2.2.2.1. 先打开文件:
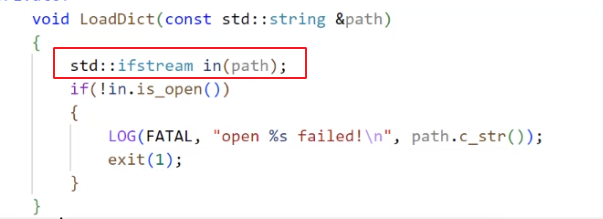
3.2.2.2.2. 如果打开失败了呢?
直接退出, 这属于一个 FATAL 错误.
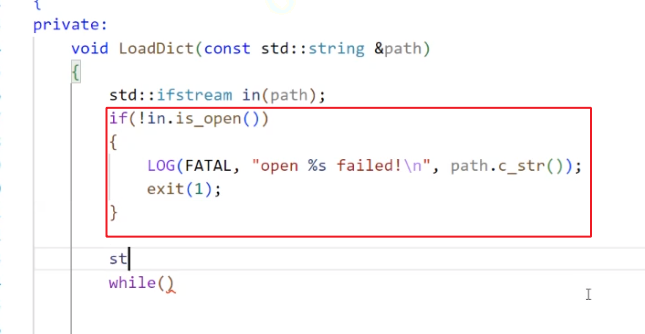
3.2.2.2.3. 打开成功呢?
我们开始从文件中读取信息.
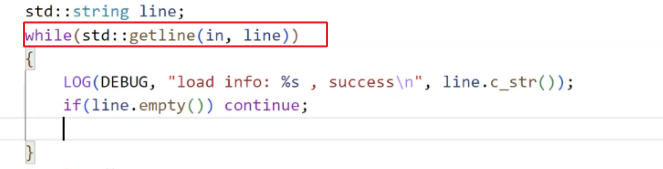
注意: 这个 getline 里面内置了强制类型转换为 bool 的功能, 因此可以用到 while 当中.
处理"异常":
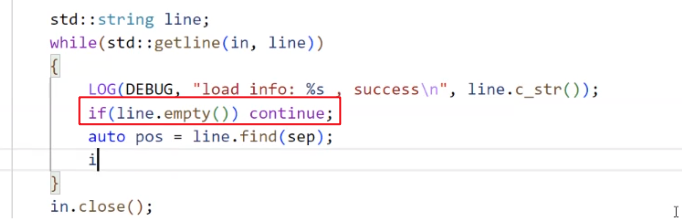
定义分隔符:
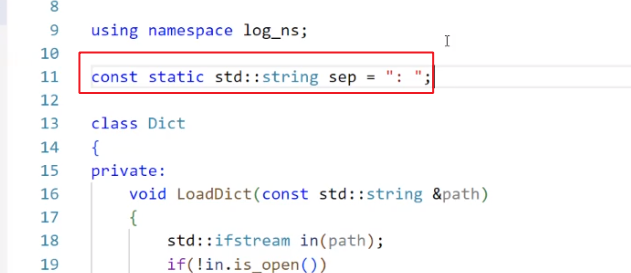

如果没有找到分隔符: 咱们直接 continue
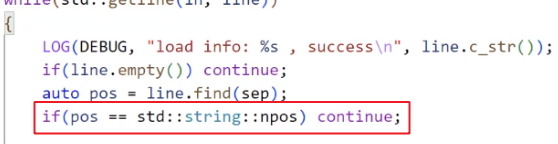
如果找到了, 咱们就截取子串.
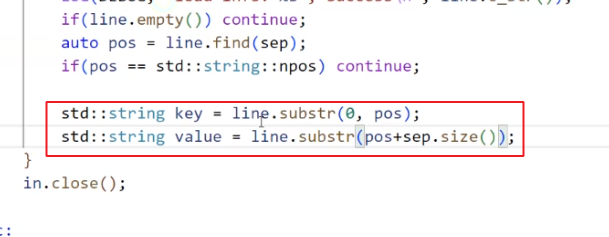
如果 key / value 为空, 我们也要 continue.

我们把 key-val 插入到 _dict 当中.

到最后, 我们再提示一下即可:

3.2.2.2.4. 最后记得关闭文件描述符 -> 防止资源泄露
in.close()
3.2.3. dict::translate()
3.2.3.1. 查找一个空单词?

3.2.3.2. 如果没查到?

3.2.3.3. 如果查到了?

3.3. 字典服务 与 服务器相关联
肯定是在 UdpServerMain.cc 当中完成的.
首先构建一个字典对象:

然后我们服务器当中需要一个什么类型的回调函数?

注意: 这个参数是非 const 的.
但是我们 dict 当中是(this, string)的, 所以我们用 bind 绑定一下.

之后, 我们再把这个函数传给我们的服务器即可.

3.4. 测试一下
启动服务端, 发现是 ok 的:

启动客户端, 也是 ok 的:


4. 参考代码
4.1. 核心代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <functional>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include "nocopy.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "InetAddr.hpp"
using namespace log_ns;
static const int gsockfd = -1;
static const uint16_t glocalport = 8888;
enum
{
SOCKET_ERROR = 1,
BIND_ERROR
};
// 解耦合: 我们约定, 客户端给我们发过来的是一个一个的单词(字符串), 对于这些字符串
// 我们不再让服务器处理了, 而是让服务器把这些任务派发给另一个函数完成, 从
// 而实现解耦合(业务与服务器通信解耦)!
// 服务器: 负责 读数据 + 发数据.
// 业务: 解耦, 负责处理数据.
using func_t = std::function<std::string(std::string)>;
// 这个就算我们的业务函数, 用包装器进行了类型包装, 设计为回调函数!
// UdpServer user("192.1.1.1", 8899);
// 一般服务器主要是用来进行网络数据读取和写入的。IO的
// 服务器IO逻辑 和 业务逻辑 解耦
class UdpServer : public nocopy
{
public:
UdpServer(func_t func, uint16_t localport = glocalport)
: _func(func),
_sockfd(gsockfd),
_localport(localport),
_isrunning(false)
{
}
void InitServer()
{
// 1. 创建socket文件
_sockfd = ::socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (_sockfd < 0)
{
LOG(FATAL, "socket error\\n");
exit(SOCKET_ERROR);
}
LOG(DEBUG, "socket create success, _sockfd: %d\\n", _sockfd); // 3
// 2. bind
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(_localport);
// local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_localip.c_str()); // 1. 需要4字节IP 2. 需要网络序列的IP — 暂时
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; // 服务器端,进行任意IP地址绑定
int n = ::bind(_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&local, sizeof(local));
if (n < 0)
{
LOG(FATAL, "bind error\\n");
exit(BIND_ERROR);
}
LOG(DEBUG, "socket bind success\\n");
}
void Start()
{
_isrunning = true;
char inbuffer[1024];
while (_isrunning)
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
ssize_t n = recvfrom(_sockfd, inbuffer, sizeof(inbuffer) – 1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len);
if (n > 0)
{
InetAddr addr(peer);
inbuffer[n] = 0;
// 一个一个的单词
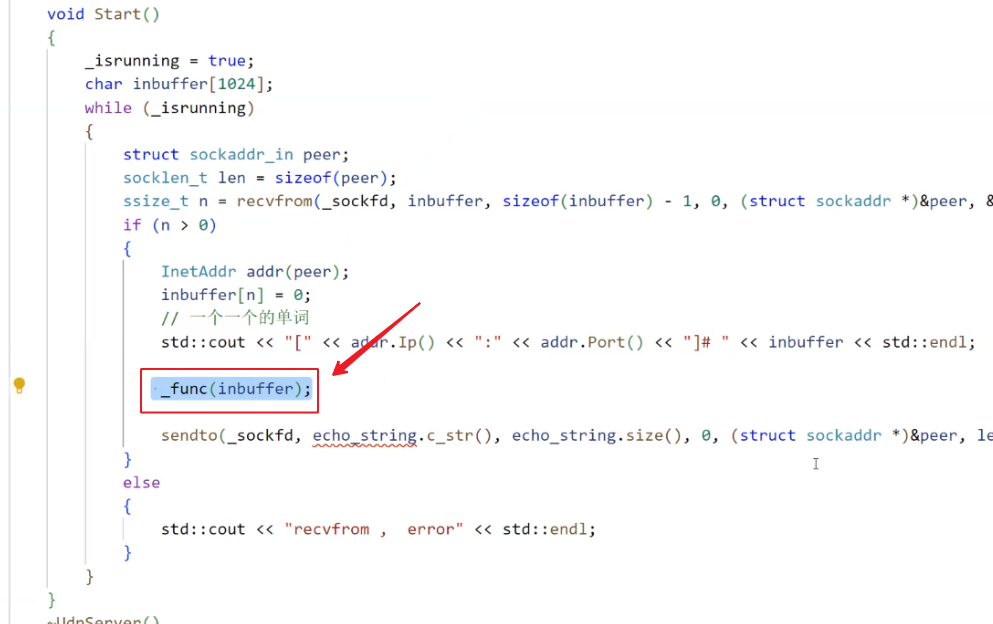
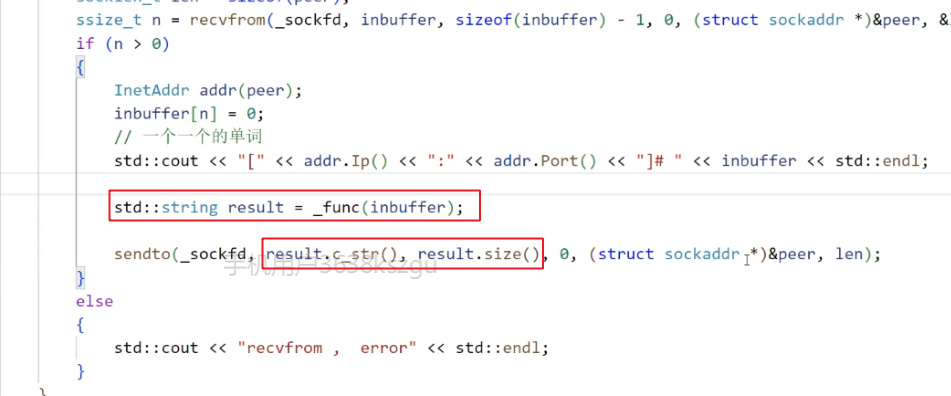
std::cout << "[" << addr.Ip() << ":" << addr.Port() << "]# " << inbuffer << std::endl;
std::string result = _func(inbuffer); // 把任务交给_func函数, 让_func函数处理, 处理完了我们服务器再给他发过去.
sendto(_sockfd, result.c_str(), result.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, len);
}
else
{
std::cout << "recvfrom , error" << std::endl;
}
}
}
~UdpServer()
{
if (_sockfd > gsockfd)
::close(_sockfd);
}
private:
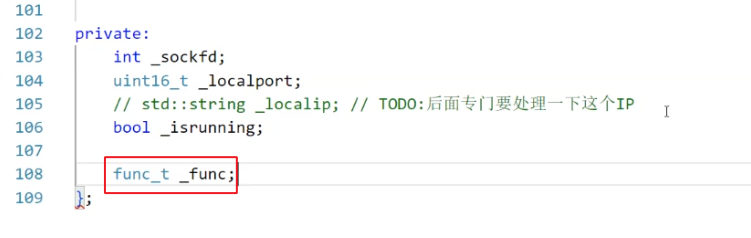
int _sockfd;
uint16_t _localport;
// std::string _localip; // TODO:后面专门要处理一下这个IP
bool _isrunning;
func_t _func; // 业务 -> 回调函数.
// 这样写回调的好处就是服务器不需要关心业务如何处理, 只需要了解服务器需要给
// 业务什么东西, 然后服务器需要让业务返回什么东西即可.
};
#include "UdpServer.hpp"
#include "Dict.hpp"
#include <memory>
// ./udp_server local-port
// ./udp_server 8888
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " local-port" << std::endl;
exit(0);
}
uint16_t port = std::stoi(argv[1]);
EnableScreen();
Dict dict("./dict.txt"); // 构建字典 + 配置文件路径进行配置加载
func_t translate = std::bind(&Dict::Translate, &dict, std::placeholders::_1); // 绑定成为指定类型: string (string).
std::unique_ptr<UdpServer> usvr = std::make_unique<UdpServer>(translate, port); //C++14的标准 -> 这样的好处就是, 业务与服务器端的解耦, 这样你想换一个业务, 只需要修改一下业务函数指向即可, 其他则不用修改!
usvr->InitServer();
usvr->Start();
return 0;
}
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "Log.hpp"
/*
* 这个字典类, 是一个业务, 用来把服务器交给我们的单词, 翻译成汉语给他返回去.
* 其中, 我们的字典需要从文件中加载对应的单词数据, 是一个文件级别的数据, 而非
* 内存级别的数据.
*/
using namespace log_ns;
const static std::string sep = ": "; // 定义分隔符.
// sad: 悲伤的
class Dict
{
private:
void LoadDict(const std::string &path)
{
std::ifstream in(path); // 打开文件
if (!in.is_open()) // 打开失败了就不可能完成任务, 直接exit!
{
LOG(FATAL, "open %s failed!\\n", path.c_str());
exit(1);
}
std::string line;
while (std::getline(in, line)) // 注意: cpp中的getline是重载了bool类型哦~
{
LOG(DEBUG, "load info: %s , success\\n", line.c_str());
if (line.empty()) // 避免空行.
continue;
auto pos = line.find(sep);
if (pos == std::string::npos) // 避免没有": "的情况.
continue;
std::string key = line.substr(0, pos);
if (key.empty()) // 如果发现key值是空, 直接忽略.
continue;
std::string value = line.substr(pos + sep.size());
if (value.empty()) // 如果发现value值是空, 直接忽略.
continue;
_dict.insert(std::make_pair(key, value)); // 用哈希将数据组织起来!
}
LOG(INFO, "load %s done\\n", path.c_str());
in.close();
}
public:
// 构造: 构造的时候 自动 把所有的文件属性加载到哈希表中去!
Dict(const std::string &dict_path) : _dict_path(dict_path)
{
LoadDict(_dict_path); // 自动加载资源到哈希表组织起来!
}
// 翻译
std::string Translate(std::string word)
{
if(word.empty()) return "None"; // 如果没有key值, 咱们就返回"None"
auto iter = _dict.find(word);
if(iter == _dict.end()) return "None"; // 没有查到, 咱们就返回"None"
else return iter->second;
}
~Dict()
{
}
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _dict; // 对于这个字典, 我们加载进来是用哈希表进行映射组织的!
std::string _dict_path; // 外界给你文件路径, 来读取对应的单词数据.
};
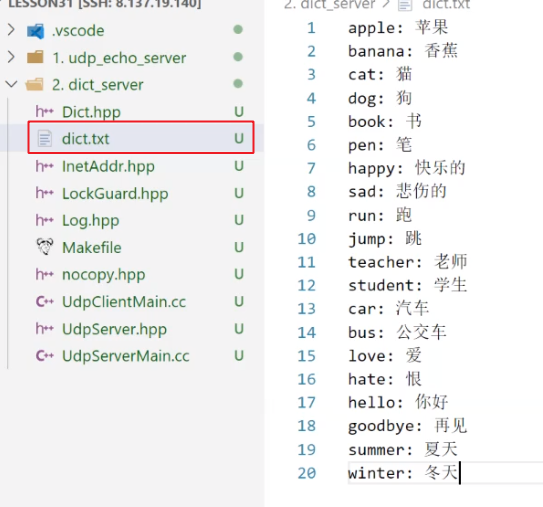
apple: 苹果
banana: 香蕉
cat: 猫
dog: 狗
book: 书
pen: 笔
happy: 快乐的
sad: 悲伤的
run: 跑
jump: 跳
teacher: 老师
student: 学生
car: 汽车
bus: 公交车
love: 爱
hate: 恨
hello: 你好
goodbye: 再见
summer: 夏天
winter: 冬天
4.2. 其他代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
class InetAddr
{
private:
void ToHost(const struct sockaddr_in &addr)
{
_port = ntohs(addr.sin_port);
_ip = inet_ntoa(addr.sin_addr);
}
public:
InetAddr(const struct sockaddr_in &addr):_addr(addr)
{
ToHost(addr);
}
std::string Ip()
{
return _ip;
}
uint16_t Port()
{
return _port;
}
~InetAddr()
{
}
private:
std::string _ip;
uint16_t _port;
struct sockaddr_in _addr;
};
#pragma once
#include <pthread.h>
class LockGuard
{
public:
LockGuard(pthread_mutex_t *mutex):_mutex(mutex)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(_mutex);
}
~LockGuard()
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(_mutex);
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t *_mutex;
};
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdarg>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstring>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "LockGuard.hpp"
namespace log_ns
{
enum
{
DEBUG = 1,
INFO,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL
};
std::string LevelToString(int level)
{
switch (level)
{
case DEBUG:
return "DEBUG";
case INFO:
return "INFO";
case WARNING:
return "WARNING";
case ERROR:
return "ERROR";
case FATAL:
return "FATAL";
default:
return "UNKNOWN";
}
}
std::string GetCurrTime()
{
time_t now = time(nullptr);
struct tm *curr_time = localtime(&now);
char buffer[128];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
curr_time->tm_year + 1900,
curr_time->tm_mon + 1,
curr_time->tm_mday,
curr_time->tm_hour,
curr_time->tm_min,
curr_time->tm_sec);
return buffer;
}
class logmessage
{
public:
std::string _level;
pid_t _id;
std::string _filename;
int _filenumber;
std::string _curr_time;
std::string _message_info;
};
#define SCREEN_TYPE 1
#define FILE_TYPE 2
const std::string glogfile = "./log.txt";
pthread_mutex_t glock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
// log.logMessage("", 12, INFO, "this is a %d message ,%f, %s hellwrodl", x, , , );
class Log
{
public:
Log(const std::string &logfile = glogfile) : _logfile(logfile), _type(SCREEN_TYPE)
{
}
void Enable(int type)
{
_type = type;
}
void FlushLogToScreen(const logmessage &lg)
{
printf("[%s][%d][%s][%d][%s] %s",
lg._level.c_str(),
lg._id,
lg._filename.c_str(),
lg._filenumber,
lg._curr_time.c_str(),
lg._message_info.c_str());
}
void FlushLogToFile(const logmessage &lg)
{
std::ofstream out(_logfile, std::ios::app);
if (!out.is_open())
return;
char logtxt[2048];
snprintf(logtxt, sizeof(logtxt), "[%s][%d][%s][%d][%s] %s",
lg._level.c_str(),
lg._id,
lg._filename.c_str(),
lg._filenumber,
lg._curr_time.c_str(),
lg._message_info.c_str());
out.write(logtxt, strlen(logtxt));
out.close();
}
void FlushLog(const logmessage &lg)
{
// 加过滤逻辑 — TODO
LockGuard lockguard(&glock);
switch (_type)
{
case SCREEN_TYPE:
FlushLogToScreen(lg);
break;
case FILE_TYPE:
FlushLogToFile(lg);
break;
}
}
void logMessage(std::string filename, int filenumber, int level, const char *format, …)
{
logmessage lg;
lg._level = LevelToString(level);
lg._id = getpid();
lg._filename = filename;
lg._filenumber = filenumber;
lg._curr_time = GetCurrTime();
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, format);
char log_info[1024];
vsnprintf(log_info, sizeof(log_info), format, ap);
va_end(ap);
lg._message_info = log_info;
// 打印出来日志
FlushLog(lg);
}
~Log()
{
}
private:
int _type;
std::string _logfile;
};
Log lg;
#define LOG(Level, Format, …) \\
do \\
{ \\
lg.logMessage(__FILE__, __LINE__, Level, Format, ##__VA_ARGS__); \\
} while (0)
#define EnableScreen() \\
do \\
{ \\
lg.Enable(SCREEN_TYPE); \\
} while (0)
#define EnableFILE() \\
do \\
{ \\
lg.Enable(FILE_TYPE); \\
} while (0)
};
.PHONY:all
all:udpserver udpclient
udpserver:UdpServerMain.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++14
udpclient:UdpClientMain.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++14
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf udpserver udpclient
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
// 客户端在未来一定要知道服务器的IP地址和端口号
// ./udp_client server-ip server-port
// ./udp_client 127.0.0.1 8888
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 3)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " server-ip server-port" << std::endl;
exit(0);
}
std::string serverip = argv[1];
uint16_t serverport = std::stoi(argv[2]);
int sockfd = ::socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if(sockfd < 0)
{
std::cerr << "create socket error" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// client的端口号,一般不让用户自己设定,而是让client OS随机选择?怎么选择,什么时候选择呢?
// client 需要 bind它自己的IP和端口, 但是client 不需要 “显示” bind它自己的IP和端口,
// client 在首次向服务器发送数据的时候,OS会自动给client bind它自己的IP和端口
struct sockaddr_in server;
memset(&server, 0, sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(serverport);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(serverip.c_str());
while(1)
{
std::string line;
std::cout << "Please Enter# ";
std::getline(std::cin, line);
// std::cout << "line message is@ " << line << std::endl;
int n = sendto(sockfd, line.c_str(), line.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&server, sizeof(server)); // 你要发送消息,你得知道你要发给谁啊!
if(n > 0)
{
struct sockaddr_in temp;
socklen_t len = sizeof(temp);
char buffer[1024];
int m = recvfrom(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&temp, &len);
if(m > 0)
{
buffer[m] = 0;
std::cout << buffer << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "recvfrom error" << std::endl;
break;
}
}
else
{
std::cout << "sendto error" << std::endl;
break;
}
}
::close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
#pragma once
class nocopy
{
public:
nocopy(){}
~nocopy(){}
nocopy(const nocopy&) = delete;
const nocopy& operator=(const nocopy&) = delete;
};
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心



评论前必须登录!
注册