服务器系统配置初始化脚本主要用于在服务器首次部署或重置后自动执行一系列预设的配置任务。这些任务旨在将服务器设置到一个已知且安全的状态,以便可以立即开始使用或部署特定的应用程序或服务。
1 问题
1)脚本无法执行或执行中断
2)配置设置错误
3)最大打开文件数设置不正确
2 分析
1)确保脚本有执行的权限、有没有语法错误、查看脚本执行过程中的错误信息,根据错误信息定位问题并修复
2)时区设置不正确、SELinux设置不正确、防火墙设置不正确
3)检查脚本中的最大打开文件数设置命令是否正确执行,
使用ulimit -n命令查看当前最大打开文件数设置
3 流程图
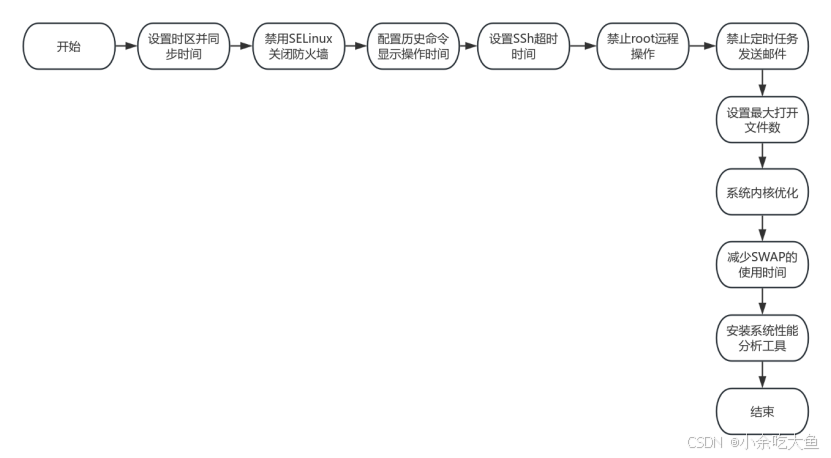
4 实现
#服务器系统配置初始化脚本
#!/bin/bash
#设置时区并同步时间
#设置时区
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
#检查是否已存在ntdate的cron作业,如果不存在则添加
if ! crontab -l | grep -q 'ntdate'; then
(
echo "* 1 * * * ntpdate time.windows.com >/dev/null 2>&1"
) | crontab –
else
echo "ntpdate的cron作业已存在,无需添加"
fi
#禁用selinux
sed -i '/SELINUX/{s/permissive/disabled/}' /etc/selinux/config
#关闭防火墙
#检查RHEL 7或更高版本
if egrep "7.[0-9]" /etc/redhat-release &>/dev/null; then
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
#检查RHEL 6或更低版本
elif egrep "6.[0-9]" /etc/redhat-release &>/dev/null; then
service iptables stop
chkconfig iptables off
fi
#历史命令显示操作时间
if ! grep -q HISTIMEFORMAT /etc/bashrc; then
echo 'export HISTIMEFORMAT="%Y-%m-%d %H-%M-%S $(whoami)"' >> /etc/bashrc
fi
#SSH超时时间
if ! grep "TMOUT=600" /etc/profile &> /dev/null; then
#服务器系统配置初始化脚本
#!/bin/bash
#设置时区并同步时间
#设置时区
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
#检查是否已存在ntdate的cron作业,如果不存在则添加
if ! crontab -l | grep -q 'ntdate'; then
(
echo "* 1 * * * ntpdate time.windows.com >/dev/null 2>&1"
) | crontab –
else
echo "ntpdate的cron作业已存在,无需添加"
fi
#禁用selinux
sed -i '/SELINUX/{s/permissive/disabled/}' /etc/selinux/config
#关闭防火墙
#检查RHEL 7或更高版本
if egrep "7.[0-9]" /etc/redhat-release &>/dev/null; then
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
#检查RHEL 6或更低版本
elif egrep "6.[0-9]" /etc/redhat-release &>/dev/null; then
service iptables stop
chkconfig iptables off
fi
#历史命令显示操作时间
if ! grep -q HISTTIMEFORMAT /etc/bashrc; then
echo 'export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%Y-%m-%d %H-%M-%S $(whoami)"' >> /etc/bashrc
fi
#SSH超时时间
if ! grep "TMOUT=600" /etc/profile &> /dev/null; then
echo "export TMOUT=600" >> /etc/profile
fi
#禁止root远程登录
sed -i '/^#*PermitRootLogin/s/#*PermitRootLogin .*/PermitRootLogin no/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
#禁止定时任务发送邮件
sed -i 's/^MAILTO=root/MAILTO=""/' /etc/crontab
#设置最大打开文件数
if ! grep "* soft nofile 65535" /etc/security/limits.conf &>/dev/null; then
cat >> /etc/security/limits.conf << EOF
*soft nofile 65535
*hard nofile 65535
EOF
fi
#系统内核优化
cat >> /etc/sysctl.conf << EOF
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies=1 #设置了TCP SYN Cookies的启用,SYN Cookies是一种防御机制
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets=20480 #设置了系统可以保持的TIME-WAIT套接字的最大数量
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog=20480 #设置了系统用于存储尚未完全建立的连接的队列的最大长度
net.core.netdev_max_backlog=262144 #设置了网络接口接收队列的最大长度
EOF
#减少SWAP的使用
echo 0 > /proc/sys/vm/swappiness
#安装系统性能分析工具
yum install gcc make autoconf vim sysstat net-tools
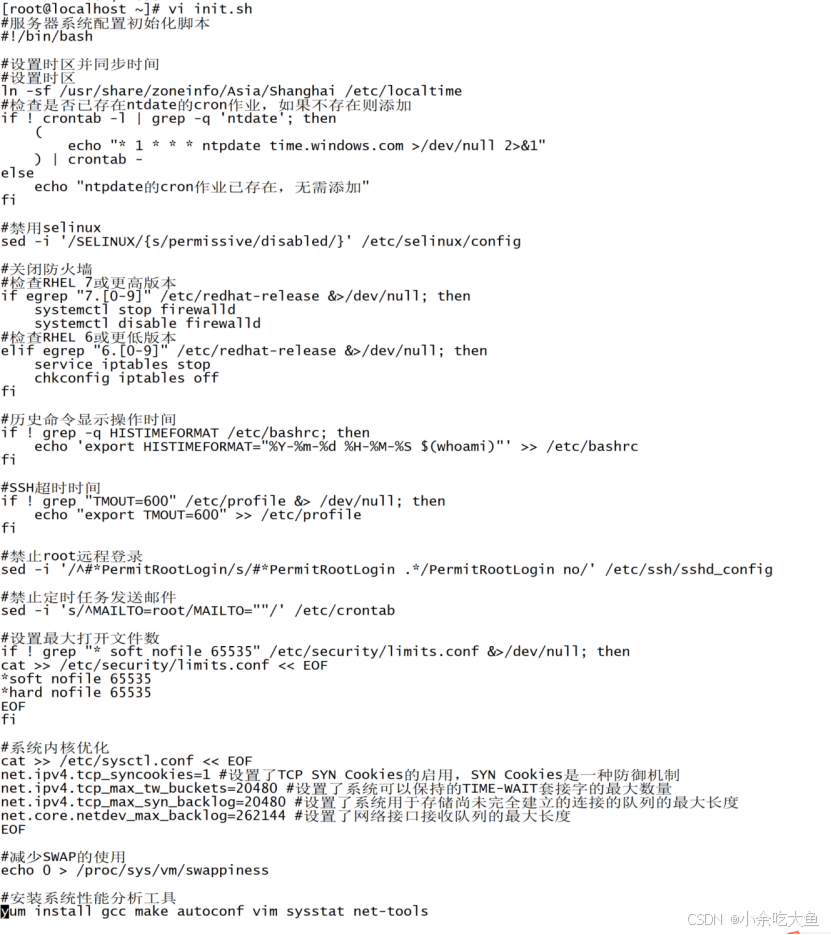
5 实现解析
1)使用ln -sf 创建软链接,/usr/share/zoneinfo/包含各个时区的信息文件,检查ntdate的cron作业(ntdate用于同步时间)
2)使用sed -i将/etc/selinux/config中的permissive替换成disabled
3)egrep命令检查版本并使用命令关闭防火墙
4)使用! grep -q 检查/etc/bashrc中是否存在HISTIMEFORMAT存在则继续执行不存在则输入
5)同理,检查TMOUT=600是否在/etc/profile,不存在则添加
6)使用sed -i命令来进行替换禁止root远程登录
7)同理替换/etc/crontab中的MAILTO禁止定时任务发送邮件
8)检查soft nofile 65535是否在/etc/security/limits.conf中,不存在则使用soft、hard命令创建软、硬链接
9)cat >> /etc/sysctl.conf << EOF接下来的输出除了遇到EOF都被读取并写入该文件中
10)swappiness参数控制着内存管理方面的行为(0~100越小是避免使用越大是积极使用)
6 验证
1)检查脚本语法,没有出现东西说明正确

2)执行脚本
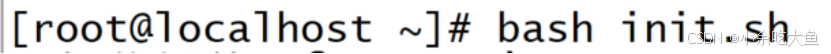
3)验证时区设置可以看到Time zone一行出现Asia/Shanghai

4)验证cron作业

5)验证SELinux状态

6)验证防火墙状态

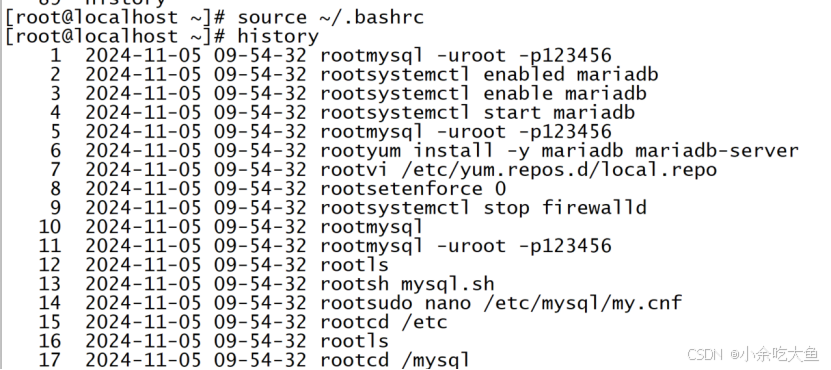
7)验证历史命令显示操作时间
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心




评论前必须登录!
注册