服务器不能上网,时间对不上,多台服务器时间不同步
- 不就校准一个时间吗?有多难?
- 该死的完美主义,先明确需求吧!
- 还提要求,先看看自己有什么?
- 好,那就开干!
-
- 1.外网NTP服务器校准内网服务器时间
- 2.内网自建NTP服务器
- 3.配置NTP客户端
- 参考资料
不就校准一个时间吗?有多难?
服务器时间不同步,最简单粗暴的方法是:直接用命令手动改时间。
timedatectl set-timezone "Asia/Shanghai"
date -s "2024-2-6 21:00:00"
先修改时区为上海,再修改时间,所以,so easy ,本文结束… 为什么?难受!这很不优雅,别问我为什么,总之无法接受
该死的完美主义,先明确需求吧!
还提要求,先看看自己有什么?
好,那就开干!
服务器1:172.0.0.1 计划作 本地 NTP 服务器 服务器2:172.0.0.2 NTP 客户端1 服务器3:172.0.0.3 NTP 客户端2 服务器4:172.0.0.4 NTP 客户端3
我的电脑:172.0.0.5 能上网,为什么,因为我有两张网卡,(192.168.1.1)
1.外网NTP服务器校准内网服务器时间
先安装个软件包,
yum install ntp
什么?装不上,都没网,代理上网不会吗?
export http_proxy=http://172.0.0.5:1556
export https_proxy=http://172.0.0.5:1556
yum install ntp
好,软件包装好了,开始校准时间。
ntpdate ntp.aliyun.com
用阿里的服务器校一校,很遗憾,服务器根本没配置DNS
6 Feb 21:09:08 ntpdate[249451]: Can't find host ntp.aliyun.com: Name or service not known (-2)
6 Feb 21:09:08 ntpdate[249451]: no servers can be used, exiting
那我自己直接用IP,用自己的电脑先看看IP
ping ntp.aliyun.com
PING ntp.aliyun.com (203.107.6.88) 56(84) bytes of data.
再校一校试试
ntpdate 203.107.6.88
还是不行。
6 Feb 21:12:53 ntpdate[60842]: no server suitable for synchronization found
没网?不可能,代理不了?果然,ntp服务使用的是UDP协议,端口为123。 那就在路由器上配个UDP端口转发,将123端口转发到203.107.6.88的123端口。 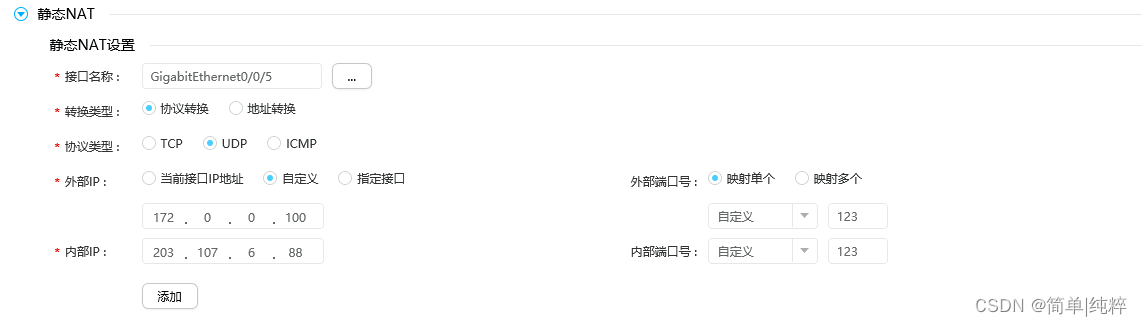 搞定! 这路由器不简单,可以NAT到互联网,简化了许多操作。没有路由器可以用其他方法,核心就是将外网的NTP服务器UDP端口123映射内网中,这时候路由器(172.0.0.100)就相当于内网的NTP服务器了。
搞定! 这路由器不简单,可以NAT到互联网,简化了许多操作。没有路由器可以用其他方法,核心就是将外网的NTP服务器UDP端口123映射内网中,这时候路由器(172.0.0.100)就相当于内网的NTP服务器了。
2.内网自建NTP服务器
以上所有服务器都能用路由器来校准时间,为什么还要内网自建NTP服务器呢?因为考虑到服务器之间的时间同步问题,内外网络环境稳定,外网波动大,路由器随时可以撤。某些场景下外网是完全隔离的。 编辑一下配置文件
vim /etc/ntp.conf
加入这两条,第一条是刚配置的转发路由器地址,第二条是它自己,当外部时间不可用时,使用本地时间。把其他不用的服务器注释即可。
# server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
# server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
# server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
# server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 172.0.0.100 iburst
server 127.127.1.0 iburst
其他看着改,完整配置文件/etc/ntp.conf
# For more information about this file, see the man pages
# ntp.conf(5), ntp_acc(5), ntp_auth(5), ntp_clock(5), ntp_misc(5), ntp_mon(5).
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift
# Permit time synchronization with our time source, but do not
# permit the source to query or modify the service on this system.
# restrict default nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
# Permit all access over the loopback interface. This could
# be tightened as well, but to do so would effect some of
# the administrative functions.
# restrict 127.0.0.1
# restrict ::1
# Hosts on local network are less restricted.
restrict 172.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
# server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
# server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
# server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
# server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 172.0.0.100 iburst
server 127.127.1.0 iburst
# fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 8
#broadcast 192.168.1.255 autokey # broadcast server
#broadcastclient # broadcast client
#broadcast 224.0.1.1 autokey # multicast server
#multicastclient 224.0.1.1 # multicast client
#manycastserver 239.255.254.254 # manycast server
#manycastclient 239.255.254.254 autokey # manycast client
# Enable public key cryptography.
#crypto
includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw
# Key file containing the keys and key identifiers used when operating
# with symmetric key cryptography.
keys /etc/ntp/keys
# Specify the key identifiers which are trusted.
#trustedkey 4 8 42
# Specify the key identifier to use with the ntpdc utility.
#requestkey 8
# Specify the key identifier to use with the ntpq utility.
#controlkey 8
# Enable writing of statistics records.
#statistics clockstats cryptostats loopstats peerstats
# Disable the monitoring facility to prevent amplification attacks using ntpdc
# monlist command when default restrict does not include the noquery flag. See
# CVE-2013-5211 for more details.
# Note: Monitoring will not be disabled with the limited restriction flag.
disable monitor
启动NTP服务,并设置开机自启
systemctl enable ntpd
systemctl start ntpd
查看一下状态
[root@server root]# ntpq -p
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
*172.0.0.1 101.207.21.141 2 u 30 128 377 43.155 7.632 2.896
LOCAL(0) .LOCL. 5 l 72m 64 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
3.配置NTP客户端
客户端比较简单,所有服务器先跟内外NTP服务器同步一下时间。
ntpdate -u 172.0.0.1
把时间同步写入硬件中
hwclock -w
每台客户机设置一个定时任务,每小时同步一下时间。
crontab -e
*/60 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 172.0.0.1 >>/tmp/ntp.log
大功告成。
参考资料
Linux系统自动校准时间 > https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45361058/article/details/101153863 centos7设置时区,时间+时间同步的三种方式 > https://blog.csdn.net/Liu__sir__/article/details/130635044 手把手教你在centos 7.4上搭建NTP服务器 > https://developer.aliyun.com/article/946051
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心




评论前必须登录!
注册